reading-notes
Operators and Loops
- Types of operators:
- assignment
- comparison
- arithmetic
- bitwise
- logicial
- bigint
- string
- conditional
- comma
- unary
- relational
- binary requires requires 2 operands, 1 before and 1 after
- unary requires a single operand
Assignment Operators
An assignment operator assigns a value to its left operand based on the value of its right operand. The simple assignment operator is equal (=), which assigns the value of its right operand to its left operand. That is, x = f() is an assignment expression that assigns the value of f() to x.
There are also compound assignment operators that are shorthand for the operations listed in the following table:
Name Shorthand operator Meaning Assignment x = f() x = f() Addition assignment x += f() x = x + f() Subtraction assignment x -= f() x = x - f() Multiplication assignment x *= f() x = x * f() Division assignment x /= f() x = x / f() Remainder assignment x %= f() x = x % f() Exponentiation assignment x **= f() x = x ** f() Left shift assignment x «= f() x = x « f() Right shift assignment x »= f() x = x » f() Unsigned right shift assignment x »>= f() x = x »> f() Bitwise AND assignment x &= f() x = x & f() Bitwise XOR assignment x ^= f() x = x ^ f() Bitwise OR assignment x |= f() x = x | f() Logical AND assignment x &&= f() x && (x = f()) Logical OR assignment x ||= f() x || (x = f()) Logical nullish assignment x ??= f() x ?? (x = f())
Cmparison operators
- compares its operands
- if true or false
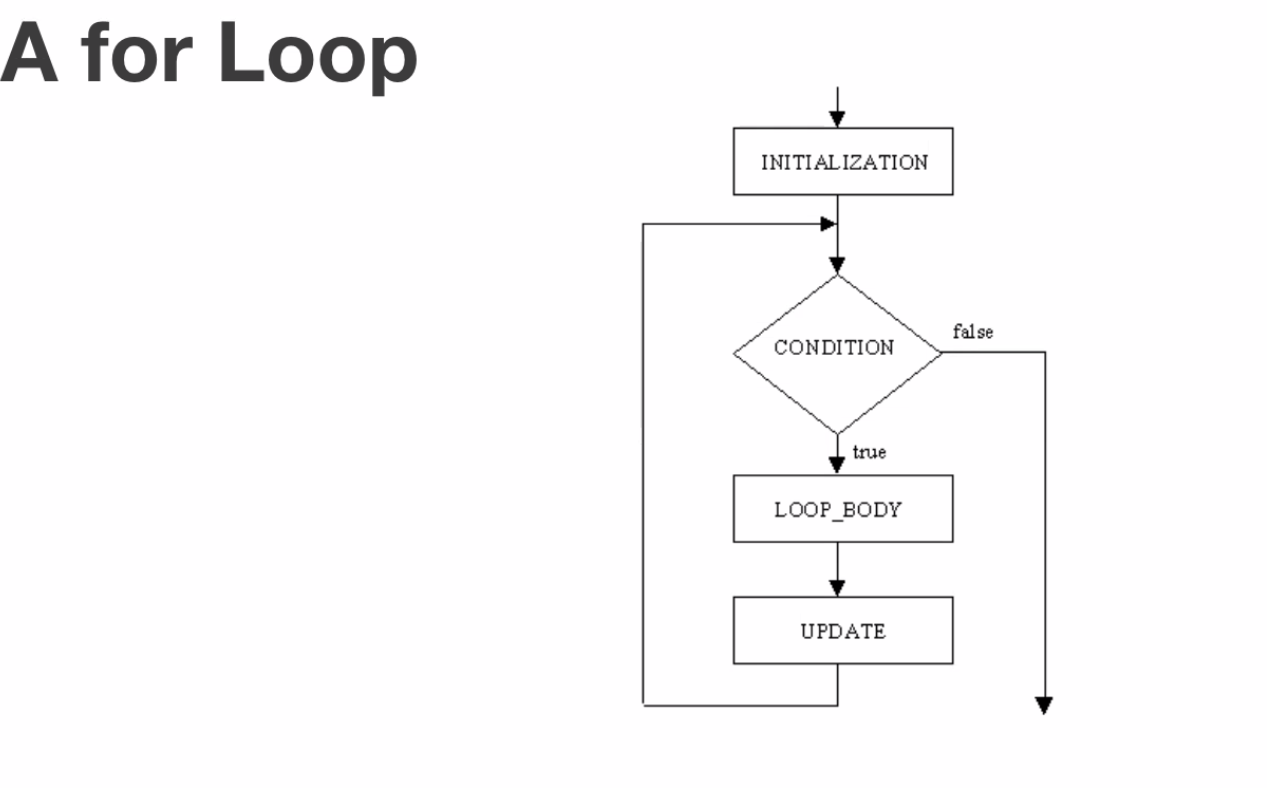
Loops
- for loops can be incremental or decremental
- ex: for (let step = 0; step < 5; step++) { // Runs 5 times, with values of step 0 through 4. console.log(‘Walking east one step’); }
- step++ means step=step+1
- this code will run 5 times until it =5 and it is no longer less than 5.
- While Loops
- while loops can very easily make infinite loops -ex: let x=0 while (x<10){ consol.log(x); x++; }
- !== means (does not) while == means (does)
- maybe can be used as a password protect to enter site?
- ex:
while(userGuess !==”yellow”){ userGuess = prompt(“wrong! Guess again”)